What Is the Difference Between Metal Sheet and Plate Metal?
In construction, manufacturing, and design industries, metal is a fundamental material. Whether you're building a skyscraper, fabricating automotive parts, or designing modern interior decor, metal plays an essential role. However, when working with metal, it's important to understand the terminology—especially when it comes to distinguishing between metal sheet and plate metal.
At first glance, the terms "sheet" and "plate" might sound interchangeable. After all, both refer to flat, rolled metal pieces. But in fact, they differ significantly in thickness, application, and fabrication processes. Understanding these differences can help ensure you select the right material for your project—both functionally and economically.
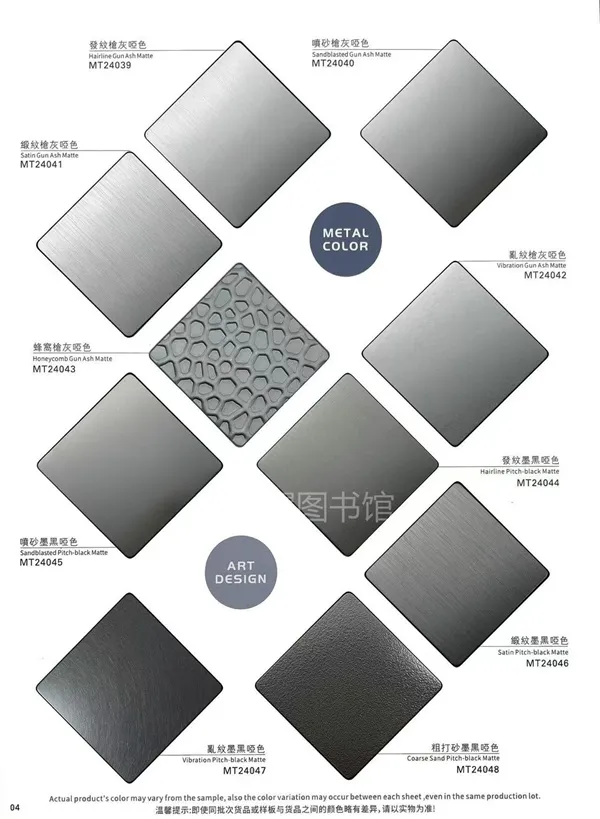

1. Definition: What Is Sheet Metal?
Sheet metal refers to a flat piece of metal that is less than 6 mm (or about 0.25 inches) thick. It is thin, lightweight, and easy to bend or cut, which makes it highly versatile in a wide range of industries.
Sheet metal is typically used in:
Automotive body panels
HVAC systems (ductwork)
Metal furniture
Enclosures and casings for electronics
Appliances
Decorative metal panels
The most common sheet metals are made from stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and carbon steel.
Sheet metal is often categorized by gauge rather than direct thickness. For example, 20-gauge steel is about 0.036 inches (0.9 mm) thick. However, keep in mind that gauge sizes differ depending on the type of metal (aluminum vs. steel, for instance).
2. Definition: What Is Plate Metal?
Plate metal, on the other hand, is any metal piece that is 6 mm (0.25 inches) or thicker. Unlike sheet metal, which is measured in gauge, plate metal is usually measured in inches or millimeters.
Because of its substantial thickness, plate metal is much stronger and more rigid. It is commonly used in:
Structural components (bridges, buildings)
Shipbuilding
Heavy machinery
Military vehicles and armor plating
Industrial equipment
Pressure vessels and pipelines
Plate metal is designed to withstand high-pressure, high-impact, or load-bearing applications, making it ideal for infrastructure and industrial settings.
3. Key Differences Between Sheet and Plate Metal
Let’s break down the major differences in a comparative way:
Feature | Sheet Metal | Plate Metal |
Thickness | < 6 mm (typically 0.5–3 mm) | ≥ 6 mm (often 6–200+ mm) |
Measurement Unit | Gauge (varies by metal type) | Inches or millimeters |
Flexibility | More flexible and bendable | Rigid and resistant to bending |
Applications | Decorative, automotive, ductwork | Structural, industrial, heavy-duty |
Fabrication | Laser cutting, stamping, folding | CNC cutting, drilling, welding |
Weight | Lightweight, easy to transport | Heavy, requires lifting equipment |
4. Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Whether to use sheet or plate metal depends on your specific application:
Use Sheet Metal When:
You need lightweight components
You’re working with decorative finishes (e.g., stainless steel panels)
You require flexible and easily formed materials
You’re focused on surface aesthetics
Use Plate Metal When:
You need structural strength
The material must resist impact or load
You're building industrial machinery, tanks, or ships
Safety and durability are top priorities
5. Common Materials Used in Sheets and Plates
The base materials are often similar across sheets and plates, but usage differs depending on form:
Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, often used for food-grade, decorative, and architectural purposes.
Carbon Steel: Strong and affordable, ideal for construction and infrastructure.
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, suitable for aerospace and electronics.
Brass/Copper: Excellent for electrical conductivity and decorative uses.
6. Finishing and Aesthetic Options for Sheet Metal
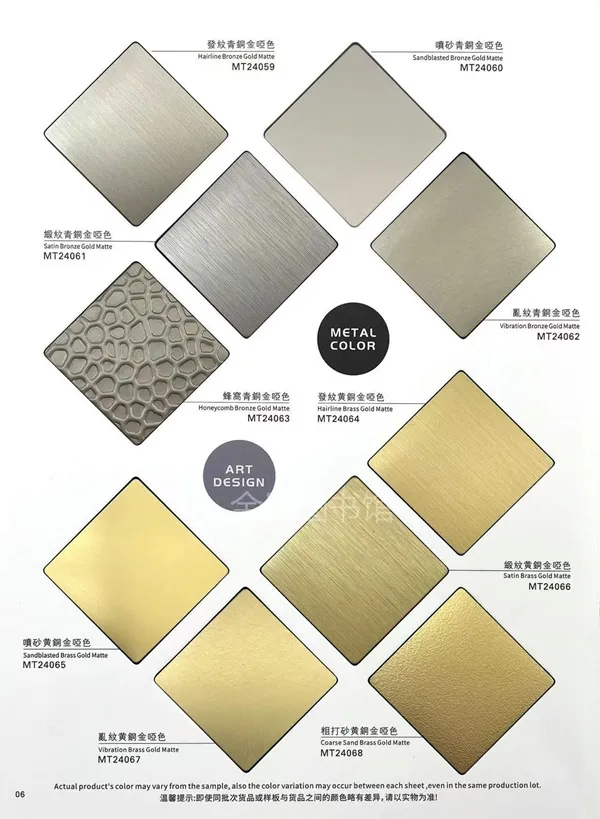
One area where sheet metal really shines—literally and figuratively—is decorative finishes. Especially in interior design, retail spaces, elevators, and signage, polished, etched, colored, or patterned sheet metal provides both function and fashion.
This brings us to a trusted supplier in the field of metal sheet design and decoration:
Meslier Metal Sheet – Redefining Surface Elegance
When it comes to premium quality decorative metal sheets, Meslier is a name you can trust. Specializing in stainless steel sheet metal with various finishes—including mirror polish, brushed texture, embossed patterns, PVD color coating, and laser etching—Meslier brings world-class surface solutions to architects, designers, and fabricators.
Why Choose Meslier Metal Sheet?
High-Quality Raw Materials: Uses 304/316-grade stainless steel for strength and corrosion resistance.
Design Flexibility: Offers a wide range of colors, textures, and patterns.
Cutting-Edge Technology: Advanced surface treatment including anti-fingerprint and PVD coating.
Wide Application: Perfect for hotel interiors, elevators, kitchens, commercial ceilings, and more.
Global Service: Supports international shipping and custom orders.
If your project requires aesthetic precision, premium quality, and expert support, Meslier Metal Sheet is your reliable partner in turning metal into art.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between metal sheet and plate metal is essential for anyone involved in fabrication, construction, or product design. By choosing the right thickness and type of metal, you ensure your project not only performs well but also looks professional. And for those seeking top-tier decorative sheet metal solutions, Meslier Metal Sheet delivers excellence in every detail.
Let me know if you’d like the Chinese translation or a localized version for your marketing platform.
Hot News

Best Stainless Steel Wine Cabinet for Home

Stainless Steel Cabinets vs. Wood Cabinets: Which is the Better Choice for Your Kitchen?

Minimalist Kitchen Design: How Stainless Steel Cabinets Fit the Trend

Creative Uses of Stainless Steel Wall Niches in Contemporary Interiors

Stainless Steel vs. Wooden Wine Cabinets: Pros & Cons

Glass Door vs. Solid Door Stainless Steel Wine Cabinets: What’s Best?

High-End vs. Budget-Friendly Stainless Steel Wine Cabinets: A Buyer’s Guide